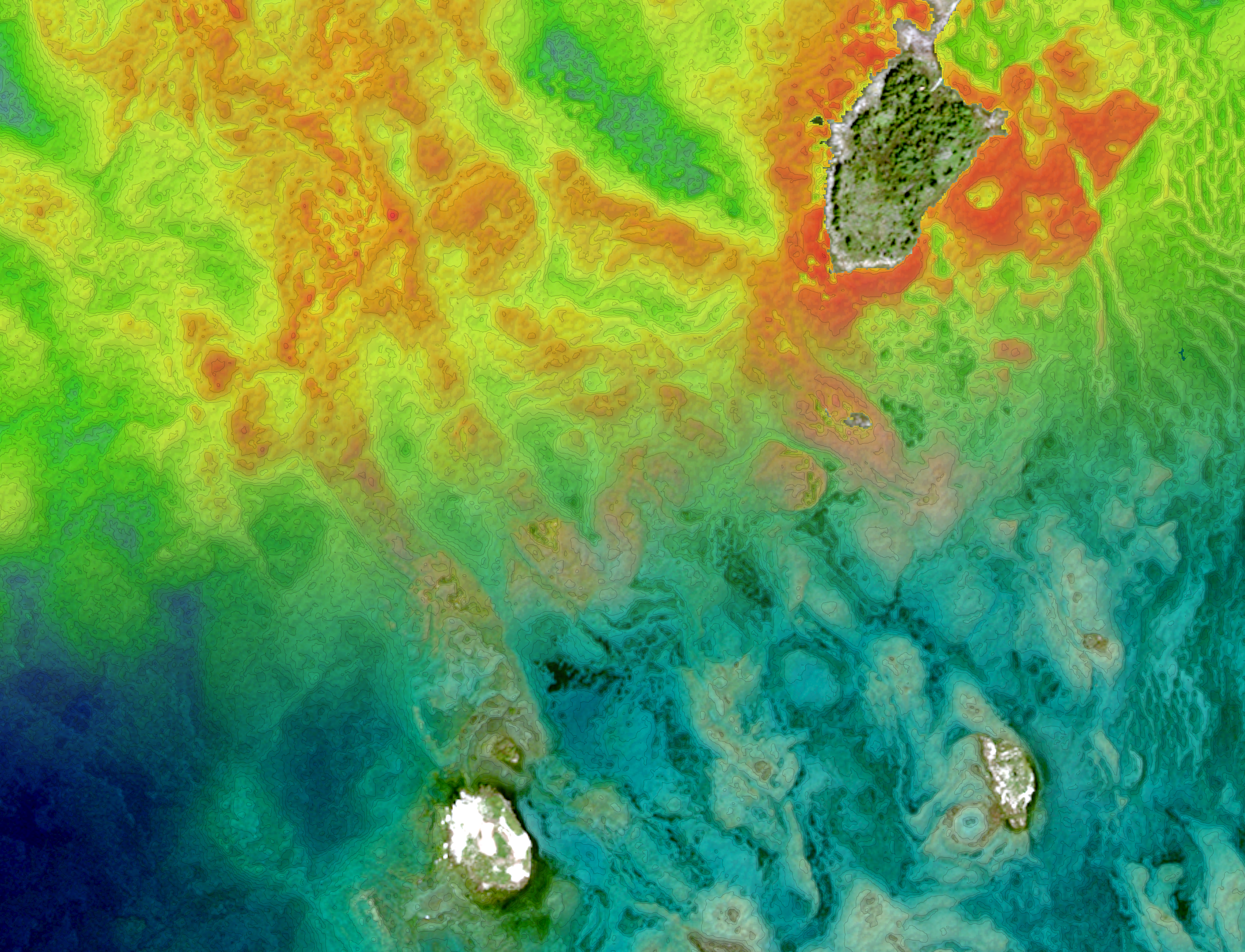
Satellite-Derived Bathymetry
In the past, bathymetry involved on-site collection techniques that made projects costly, time-consuming and unwieldy for many organizations. But with recent advances in technology and the development of satellite derived bathymetry, gathering water-depth data is fast, accurate, and reliable. Performed remotely, SDB also eliminates environmental impact, mobilization costs and risk to personnel, vessels, and equipment.
TCarta produces SDB in diverse and remote environments, providing data for shallow-water regions that are difficult or impossible to access via traditional survey vessels. Delivering SDB quickly at a fraction of traditional surveying costs, we serve governments, international hydrographic offices, engineering firms, environmental organizations, and many other customers.
SDB served as an ideal instructional tool because it integrates multiple state-of-the-art technologies, many new to hydrography. “SDB fills the gap in shallow-water data collection where it’s too risky to operate traditional bathymetric survey technology,” – Hydro International
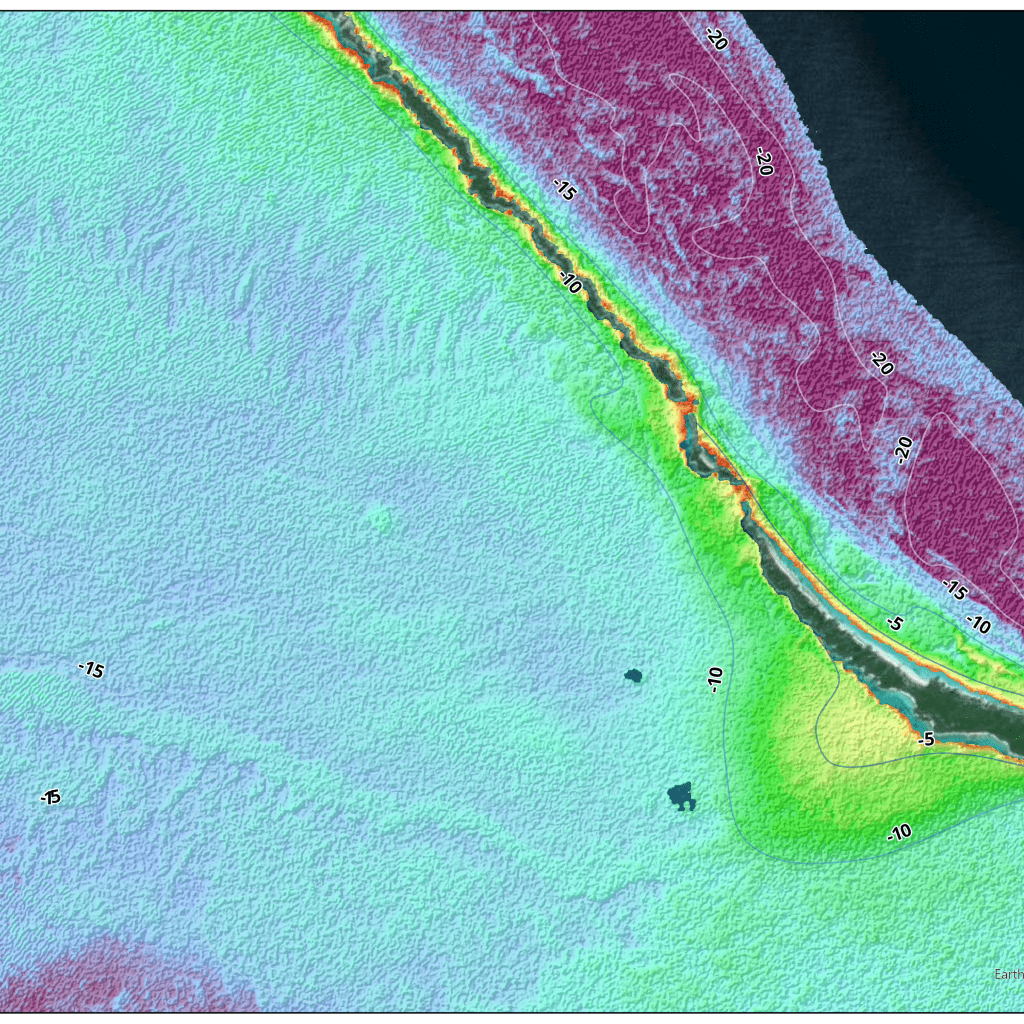
HOW IT WORKS
Multispectral images gathered by Earth-observing satellites provide the raw material for satellite-derived bathymetry (SDB) production. Digital sensors aboard the satellites capture light reflected off the Earth’s surface in multiple wavelengths. By applying proprietary algorithms to wavelengths in different parts of the imagery’s spectral range, TCarta’s remote-sensing analysts extract water-depth measurements to produce SDB outputs.
QUALITY AND SPECIFICATIONS
Quality control and quality assurance are critical in ensuring Satellite-Derived Bathymetry (SDB) consistency. TCarta’s team of hydrographic experts rigorously check data output to produce SDB to exact requirements. In Situ data is essential to the quality of SDB outputs, and TCarta’s vast library of ICESat-2 bathymetry and global chart and survey data serve as calibration and validation data for the accuracy of final products.

